Node-Red
Node-RED is a process-oriented programming tool that allows you to effortlessly connect IoT devices, APIs and online services together. It employs a browser-based editor which allows users to drag and drop different nodes onto a canvas, and connect them to create a flow. Node-RED also offers a plethora of nodes which enable users to easily interact with a diverse range of devices and services.https://Node-Red.org/。
Integrating a Node-RED project
Developing an application
Reference to:steedos-project-template.git
Executing
We can see the package.json file in the newly created node-red-app folder, which is an independent NPM project. To run the Node-Red project, we need to cd to that folder, execute yarn to install the project dependencies, and finally execute yarn start.
Once running successfully, the service can be accessed through the address with port 1880.
Static Resource Storage
we need to store static resources, we can create a static resource directory under the node-red-app folder with a self-chosen file name. Here, we use "public" as an example. At the same time, add the following code to the setting.js file under the node-red-app folder:
httpStatic: path.join(__dirname, 'public'),
httpAdminRoot: "/admin"
example:
To access the stored resources, the URL only needs to be accessed using "/". The URL for the Node-Red control page has been changed to:http://127.0.0.1:1880/admin

Initialization Configuration
After running the Node-Red service, we can access the Node-Red by entering the address displayed on the console in a browser. Upon the first access to the service, we will see an initialization configuration wizard interface, where we can set up the account and password for accessing the Node-Red service, etc. We only need to follow the prompts to complete the configuration.
After completing the initialization configuration, we will be automatically redirected to the homepage named "Node-RED on Steedos". On this page, we can see a tutorial on how to customize Node-Red.
Flow Designer
On the homepage of the running Node-Red service, we can see a button named "Go to your Node-RED flow editor" on the right side. Clicking on it will open an editor named "Flow Builder". We can access the official Node-Red website tutorial at https://Node-Red.org/docs/user-guide/ to learn how to configure, debug, and deploy flows in the editor.
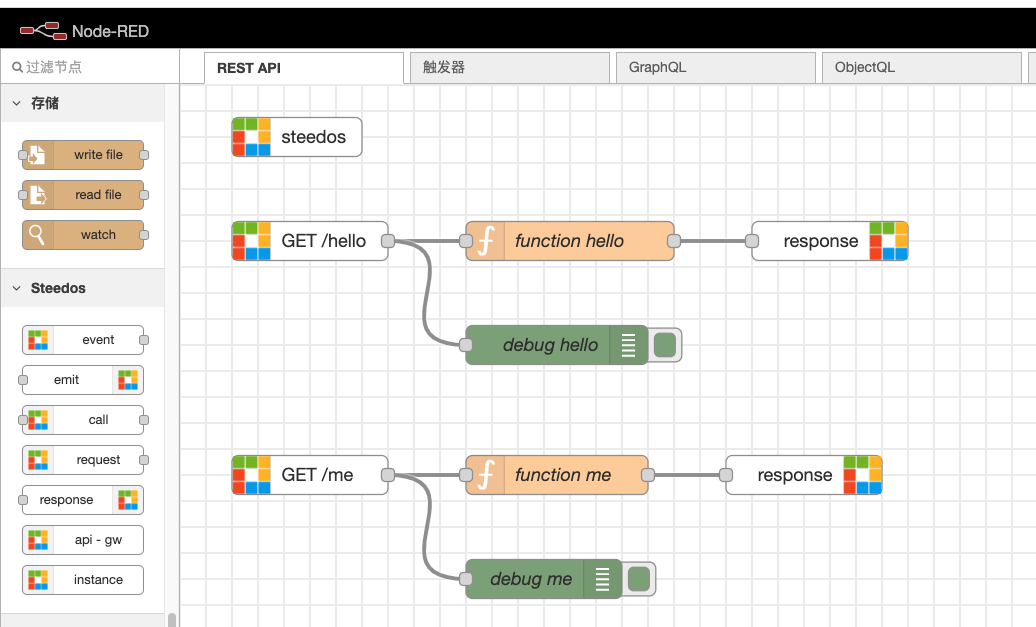
Steedos Node
We can use the aforementioned Flow Designer to configure the integration of existing business systems. If we need to connect mainstream business systems such as SAP, UFIDA, and Kingdee to integrate related businesses into Steedos, we can use a variety of nodes specially developed by us, which can easily realize various integration business requirements.
steedos-event
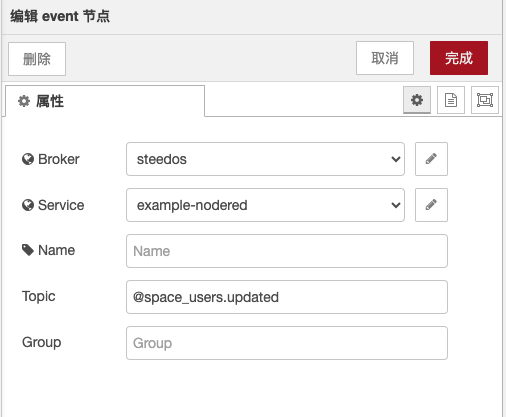
Steedos Event refers to the function of event subscription and publication using the Steedos Event service in the Steedos platform. Through Steedos Event, we can subscribe to specific events, such as record creation, update or deletion events, in order to execute custom operations when the events occur. In Steedos Event, we need to specify the following parameters:
Broker:a parameter used in Node-RED to specify the message broker used. In Node-RED, we can connect to Steedos projects by configuring the broker. Usually, NATS is used as the message broker. To configure the broker, we need to make corresponding configurations in the .env file under the Node-RED-app folder and reference it in Node-RED. For more details about NATS as a message broker, please refer to the following link:https://moleculer.services/zh/docs/0.14/networking.html#NATS-Transporter。- Service:specifies the name of the service used.
- Name:specifies the name of the node, such as the name of the node subscribing to events.
- Topic:specifies the topic or event name to subscribe to, such as creating records or updating records.
- Group:specifies the group where events are subscribed, which can be one or more groups separated by commas.
By configuring these parameters, we can use Steedos Event in the Steedos platform to implement the function of event subscription and publication, so as to execute custom operations when events occur. For example, we can subscribe to record creation events, and send notifications to Slack or WeChat when events occur, or execute custom JavaScript code when events occur to achieve more complex operations.
steedos-emit
Steedos Emit is a node within Node-RED, used for sending event messages to the Steedos project. This node requires the following parameters to be configured:
- Broker: Specifies the name of the message broker being used;
- Name: Specifies the name of the node;
- Topic: Specifies the event topic/name, which can be overridden by msg.topic;
- Broadcast: Specifies whether the event should be broadcast, which can be overridden by msg.broadcast;
- Group: Specifies the group(s) to which the event belongs, with multiple group names separated by commas. This can be overridden by msg.group.
By configuring these parameters, we can use the Steedos Emit node in Node-RED to send event messages to the Steedos project, enabling communication between different components.
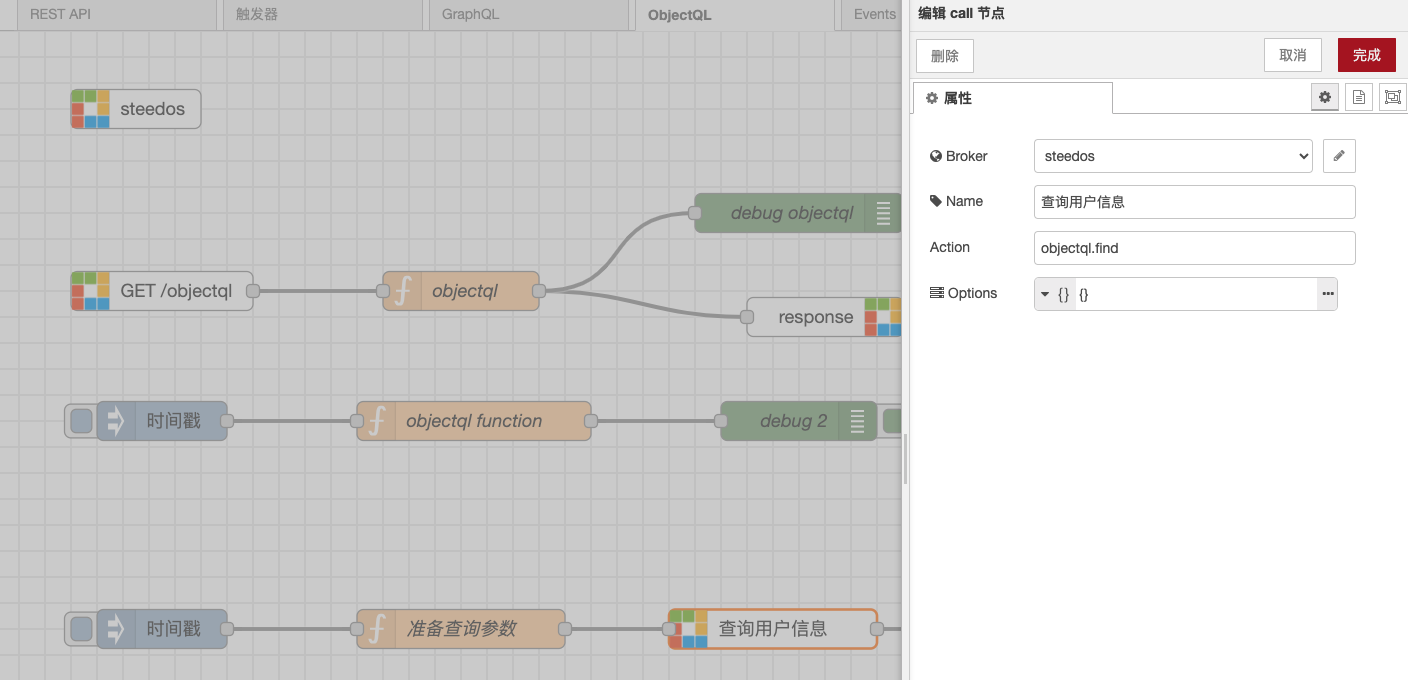
steedos-call
Steedos Call is a Node-RED node used for invoking the APIs provided by the Steedos platform. It can invoke the APIs of the Steedos platform by configuring Broker and Action. The value of Action can also be overridden by the msg.action property. Additionally, some JSON format options can be set in Options to better control the behavior of API invocation. For more information on the APIs provided by the Steedos platform, please refer to the API documentation of the Steedos platform. You can find more information about this in the steedos-template project.
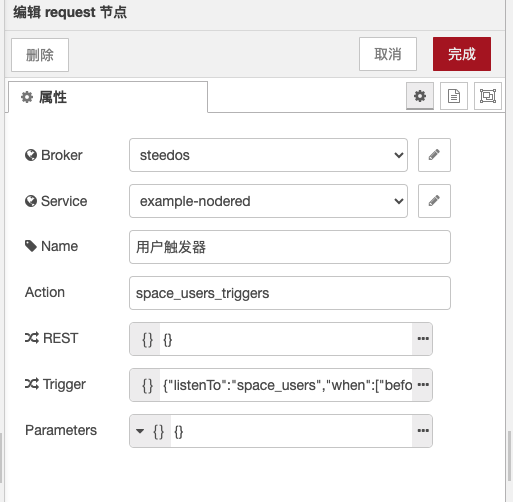
steedos-request
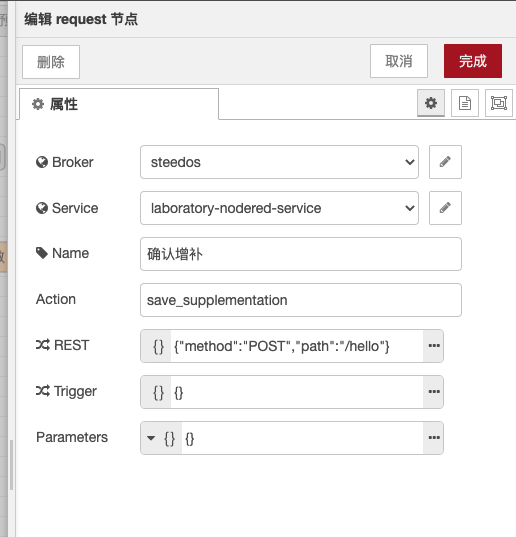
Steedos Request is a Node-RED node used for sending HTTP requests to the ObjectQL microservices and GraphQL microservices of the Steedos platform. This node requires the following parameters to be configured:
- Broker: Message broker.
- Service: Name of the microservice to be called.
- Name: The name of the node, used to identify the node within Node-RED.
- Action: The name of the operation to be performed, such as querying, creating, updating, or deleting objects. If the msg.action property is included in the message, it will override this parameter.
- REST: This attribute can customize the API according to JSON values. The "method" is the request method and the "path" is the routing URL address.
- Trigger:This attribute can customize the trigger according to JSON values. The "listenTo" is the object being listened to, and the "when" is the triggering timing. Detailed values can be found in the trigger section of the official documentation of the Steedos platform:https://beta.steedos.cn/docs/developer/action-trigger
When the node receives input messages, it sends the data in the messages as parameters for the request to the Steedos platform and sends the response data as output messages to the next node. You can find more information about this in the steedos-template project.
For example, you can customize an API in Node-RED with Steedos Request.
The API Endpoint:http://127.0.0.1:5000/service/api/example-service/+path
Example:
steedos-response
Steedos Response is a Node-RED node used for sending response messages to the initiator of an HTTP request. This node requires the following parameters to be configured:
- Name: The name of the node, used to identify the node within Node-RED.
When the node receives input messages, it sends the data in the messages back to the initiator of the HTTP request as the response body. The options of the node can be configured to set the status code, HTTP headers, and content type of the response. This node is typically used in conjunction with the Steedos Request node to respond to requests from the ObjectQL microservices and GraphQL microservices of the Steedos platform. More details can be found in the steedos-template project.
steedos-api-gw
Steedos API Gateway (APIGW) is an open-source API gateway in Steedos that helps enterprises integrate multiple microservices into a unified API.
-
Broker:refers to the message broker -
Name:specifies the name of the node -
Action: is the name of the operation to be performed
It provides a range of functionalities, such as API management, security authentication, traffic control, logging, and monitoring. In Steedos, APIGW is an independent service that can be configured through configuration files and used in conjunction with other services. This node requires the following parameters. More details can be found in the steedos-template project.
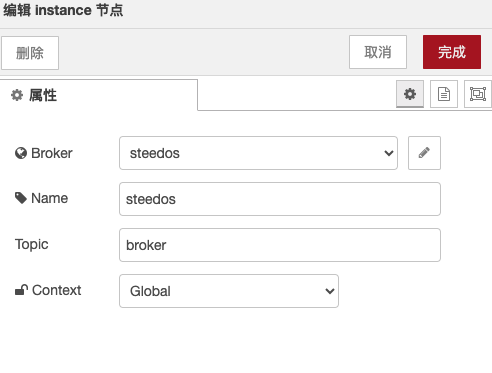
steedos-instance
Steedos Instance is a Node-RED node that allows you to inject a Steedos instance into the flow or global context. It enables you to perform various operations using the API of the Steedos platform, such as querying, creating, updating, and deleting data.
Before using the Steedos Instance node, you need to create an application on the Steedos platform and configure its data model. Then, you need to specify the name of the application and the access token in the configuration of the Steedos Instance node. This way, when you call the Steedos instance in the flow or global context, it will automatically authenticate you with the credentials you provide and allow you to perform application-related operations. More details can be found in the steedos-template project.
To invoke GraphQL
use msg.call in your Node-RED flow.
msg.call('api.graphql',
{
query: `query {
space_users(filters: ["user", "=", "${msg.meta.user.userId}"]) {
name
organization
}
}`
},
{ meta: { } }
).then((data) => {
msg.payload = data
node.send(msg)
}).catch((err) => {
node.error(err, msg)
})
To invoke ObjectQL
There are two ways to invoke ObjectQL in Node-RED:
Invoke using msg.call
msg.call('objectql.find',
{
"objectName": "space_users",
"query": {
// "fields": ["name", "orgranizations"],
"filters": ["user", "=", msg.meta.user.userId]
}
},
{ meta: {} }
).then((data) => {
msg.payload = data
node.send(msg)
}).catch((err) => {
node.error(err, msg)
})
Invoke using a broker
const broker = global.get('broker');
msg.payload = await broker.call('objectql.find',
{
"objectName": "space_users",
"query": {
"fields": ["name", "organizations"]
}
},
{ meta: {} }
)
Trigger
Example:
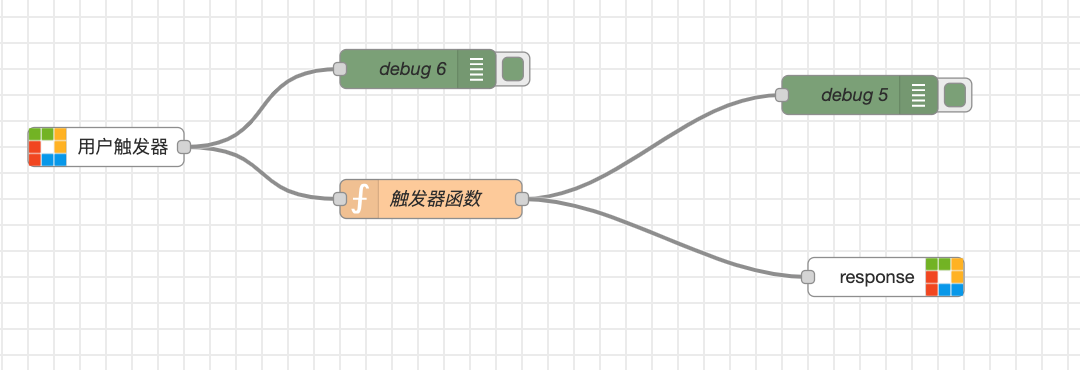
[
{
"id": "7350d7b42b233ab6",
"type": "steedos-request-action",
"z": "c10017b236a162fd",
"broker": "ce147b46c731d342",
"service": "5ab5acead56ffaea",
"name": "trigger",
"topic": "space_users_triggers",
"rest": "{}",
"restType": "json",
"trigger": "{\"listenTo\":\"space_users\",\"when\":[\"beforeInsert\",\"beforeUpdate\"]}",
"triggerType": "json",
"params": "{}",
"paramsType": "json",
"x": 100,
"y": 120,
"wires": [
[
"0441d3a1237dcd50",
"6f988203ee0b8323"
]
]
},
{
"id": "0441d3a1237dcd50",
"type": "function",
"z": "c10017b236a162fd",
"name": "trigger",
"func": "const doc = msg.payload.doc;\nif ([doc.name](http://doc.name/) && doc.name.length < 2) {\n msg.error = { message: \"姓名最少两位.\" };\n}\n\nreturn msg;",
"outputs": 1,
"noerr": 0,
"initialize": "",
"finalize": "",
"libs": [],
"x": 350,
"y": 160,
"wires": [
[
"dd4a70227645def5",
"1a4631e22fdbdc5d"
]
]
},
{
"id": "dd4a70227645def5",
"type": "debug",
"z": "c10017b236a162fd",
"name": "debug 5",
"active": true,
"tosidebar": true,
"console": false,
"tostatus": false,
"complete": "error",
"targetType": "msg",
"statusVal": "",
"statusType": "auto",
"x": 680,
"y": 80,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "1a4631e22fdbdc5d",
"type": "steedos-response-action",
"z": "c10017b236a162fd",
"name": "",
"x": 700,
"y": 220,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "6f988203ee0b8323",
"type": "debug",
"z": "c10017b236a162fd",
"name": "debug 6",
"active": true,
"tosidebar": true,
"console": false,
"tostatus": false,
"complete": "payload",
"targetType": "msg",
"statusVal": "",
"statusType": "auto",
"x": 340,
"y": 60,
"wires": []
},
{
"id": "ce147b46c731d342",
"type": "steedos-config",
"name": "steedos",
"transporter": "${TRANSPORTER}",
"namespace": "steedos",
"options": "{}",
"optionsType": "json"
},
{
"id": "5ab5acead56ffaea",
"type": "steedos-service-config",
"name": "example-nodered",
"version": "",
"settings": "{}",
"rest": "",
"settingsType": "json"
}
]
