Event Actions
In AMIS, events and actions are key to implementing complex UI interactions. They allow developers to listen for component events and respond with corresponding actions without worrying about component hierarchy. The capabilities of events and actions include, but are not limited to:
HTTP Requests: Sending HTTP requests.Popup Notifications: Executing popups, drawer openings, and Toast notifications.Page Navigation: Implementing page link navigation.Browser Operations: Includes back, forward, refresh, etc.Component Refresh: Linkage refresh of form data, i.e., data reloaded.Component State Control: Controlling the display/hide, enable/disable, and view/edit states of a specified component.Component-Specific Actions: Executing proprietary actions of a specified component, such as submitting a form.Component Data Update: Updating the data domain of a specified component.Broadcast: Multiple components listen to the same event and respond differently.JS Scripts: Implementing required logic by writing JS code snippets, also supports executing actions within JS code.Logic Orchestration: Logical operations such as conditions, loops, exclusivity, parallelism, etc.
Basic Usage
The onEvent property can be used to bind renderer events to response actions. Within onEvent, configure the event and action mapping relationship, where actions is a collection of response actions corresponding to the event.
The event system is the cornerstone of implementing interactive logic in AMIS. It allows developers to listen to and respond to user actions or system-triggered events. This section will delve into AMIS's event system, including types of events, listening, and handling.
For example: Listen to the click event of a button and execute a toast action. The code is as follows:
Events usually carry parameters, which contain information related to the event. Here it is passed through args.
{
"type": "page",
"body": [
{
"type": "button",
"label": "Toggle",
"onEvent": {
"click": {
"actions": [
{
"actionType": "toast",
"args": {
"msg": "I am a global message"
}
}
]
}
},
"id": "u:e127ddcd70c4"
}
],
"id": "u:94c822247387"
}
Context
When executing actions, you can obtain the event object's data through ${event.data} and the component's current data domain through ${__rendererData}.
Runtime Log
View the runtime log in the browser console to see the process and result of the action execution.
Classification of Events and Actions
Events include renderer events and broadcast events. Actions include general actions, component actions, broadcast actions, and custom actions, which can be specified by configuring actionType.
Triggering General Actions
General actions include sending HTTP requests, jumping links, browser operations, popup notifications, copying, sending emails, refreshing, controlling display and hide, controlling enable and disable states, updating data, etc.
Triggering Component's Actions
Trigger specific component's actions by configuring componentId or componentName.
Triggering Broadcast Actions
Implement triggering a broadcast by configuring actionType: 'broadcast'.
Orchestration of Actions
Implement action orchestration by configuring different logical actions, supporting nesting.
More Events
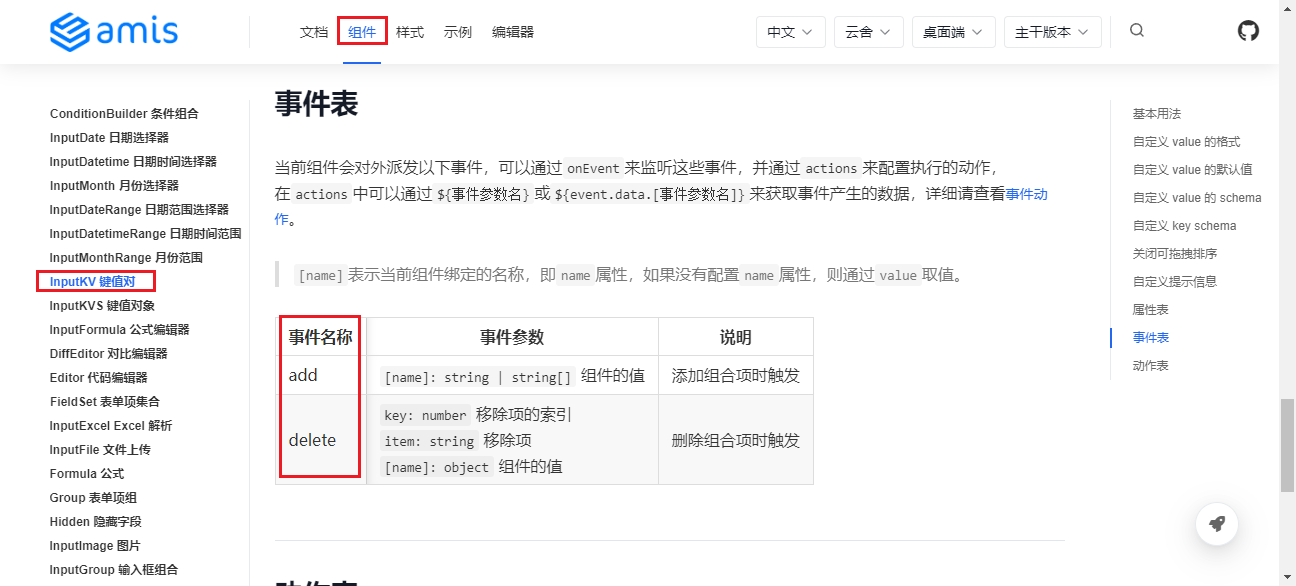
On the AMIS official website's "Components" page, you can find more events that each component can trigger. For example, for the key-value pair component, you can find the corresponding component introduction page, then scroll to the "Event Table" section. You can see there are add and delete events.
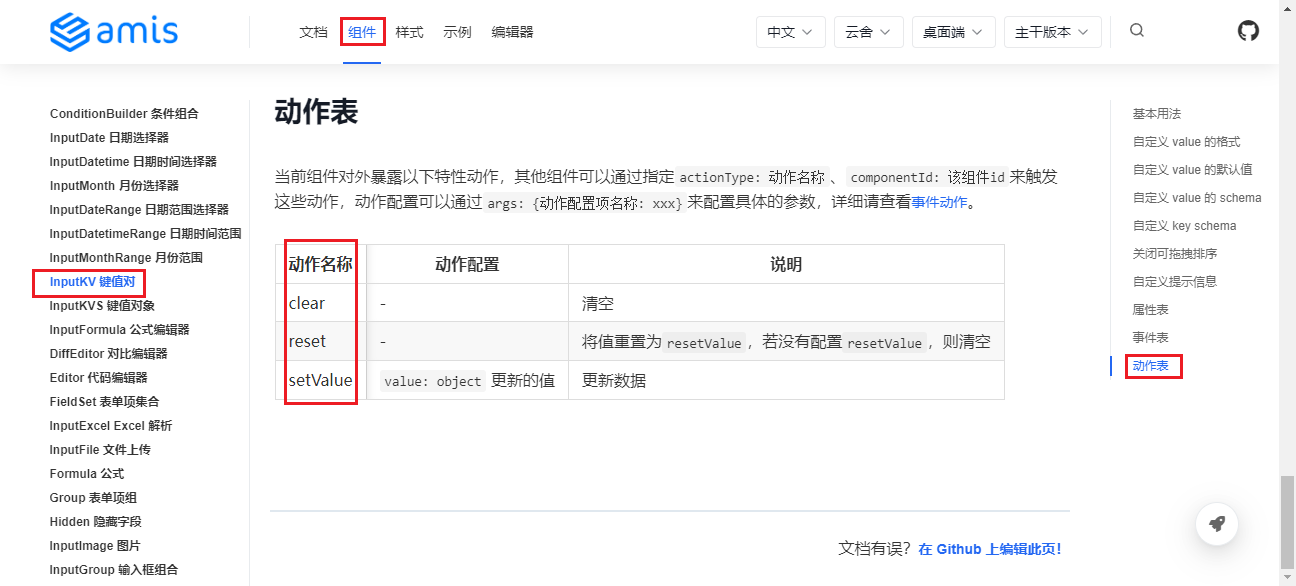
More Actions
- Triggering General Actions: Can be found on the AMIS official website at amis event actions - triggering general actions.
- Component-Specific Actions: Can be found on the component detail page.
References
Through this section, you should have a basic understanding of the AMIS event system. Mastering event listening and handling will enable you to build dynamic interfaces that respond to user operations. In the following chapters, we will explore how to combine the event system with other features of AMIS to implement more complex interaction logic.
